Consuming & Producing Kafka event
This post explain how to interact with AppConnect Designer through Kafka using the APpConnect Designer Kafka connector with an AVRO schema registry.
IBM AppConnect Designer has a Kafka Connector that allows to send messages to a Kafka Broker.
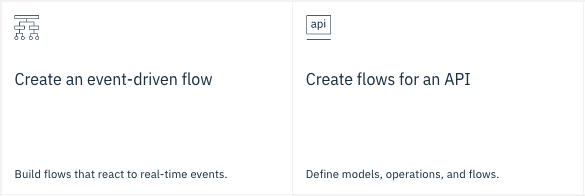
Using the wizard “Create Flows for an API” can be used to easily expose a Kafka Topic as a REST API.
The Kafka connector can also be used to trigger an AppConnect Designer flow using the wizard “Create an event-driven flow”.
It can then be used to update a SalesForce lead when a new event is published on the Kafka Topic.
The connector allows to specify a schema based on JSON or AVRO schema .
notes that IBM Event Streams registry only support AVRO schema.
The schema is defined on the connector by referencing a schema registry that can be either Confluent or Apicurio.
The last version of EventStreams registry is based on Apicurio. Note that the REST API used to get the schema from the embedded EventStreams does not include the basePath “/api”. (see later for more details)
The schema can be used to assure that the message payload format is the one that we expect. More over when this is configured, the App Connect flow is able to parse the message and provides the ability to map the fields.
Tutorial can be found in the AppConnect Designer blog and in the AppConnect Designer Knowledge Center
AppConnect Designer configuration
The configuration of the connector is made using the UI and by creating an “account” for the connector. This account can be reused afterwards to configure other connectors.
The different options and how to configure it is described in the AppConnect Designer knowledge center.
To connect to the Kafka broker provided by EventStreams, the recommended approach is to use the security mechanism SASL_SSL.
You will need (details information can be found in my post Event Endpoint Management):
- the bootstrap server url (which is available through the ES UI)
- The Kafka user and password generated by ES
- The Kafka broker certificate (this one can be downloaded from the ES UI)
- Security mechanism: SCRAM-SHA-512
Note that AppConnect Designer does not support SSL With Mutual authentication. As the ES SSL configuration is setup with mutual authentication, this mechanism is not appropriate and I would recommend to use SASL_SSL where the Kafka broker certificate needs to be provided for the SSL initialization (without mutual authentication).
The EventStreams Listener security configuration can be find back by looking at the Kubernetes Config Map “<Kafka-cluster-name>-Kafka-Config”.
To be able to use AVRO schema, the required registry configuration needs to be provided. Please note that for Apicurio registry, AppConnect Designer is designed to use by default the Apicurio REST API with the base path “/api” (f.e {hostName}/api/artifacts).
The current EventStreams registry, even if it is based on Apicurio, can not be used directly from AppConnect Designer because it does not expose the full set of the Apicurio registry REST API:
- the base path “/api” has been dropped
- example of REST API used by AppConnect Designer that is not exposed: “/ccompat/schemas/types”
Please note that this is valid for the current implementation of ES, it might be possible to the full REST API will be made available in subsequent release.
If you still want to access directly the ES registry this might be possible by exposing the registry deployed in the Apicurio-Registry container of the <ES-Name>-ibm-es-ac-uid pod through a Kubernetes service. But you will need to set appropriate security.
Connection to the registry can be tested using curl. The ES registry is exposed through SASL_SCRAM. Example of Curl:
Curl -k -u kafka-user:kafka-pwd https://<es-registry-host>/api/artifacts
Once the connector is configured, it is possible to retrieve the available Topic created on Event Streams and the schemas available in the registry:
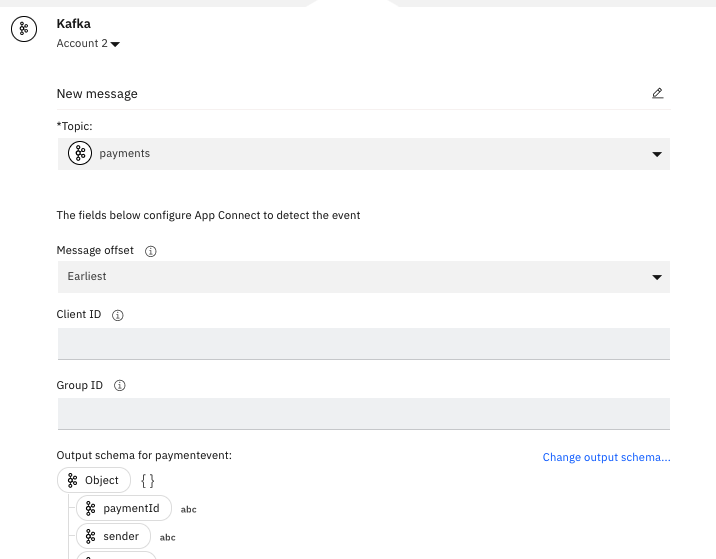
The AppConnect Designer accounts used to connect to Kafka Broker are stored in a Kubernetes secret: {appconnect-designer-name}.designer.acc

Message payload Layout
When using an AVRO schema with AppConnect Designer, the message payload is serialized and deserialized as binary encoded data using the same wire format as the confluent format:
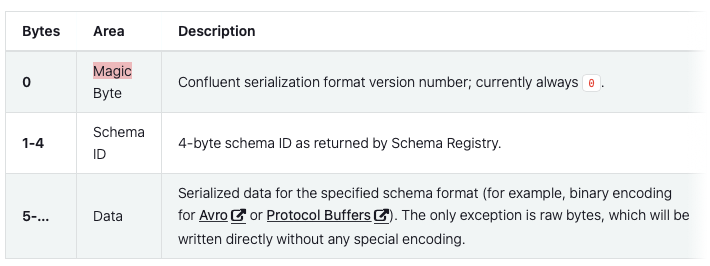
If you plan to interact with AppConnect Designer through Kafka with AVRO Schema, you need to follow this wire format. In Java this can be achieved by using the SerDes library from confluent or using a generic avro serializer.
The following code provides an example to consume a Kafka message sent by AppConnect Designer with an Avro Schema using Java with the generic Avro SerDes.
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.CommonClientConfigs;
import org.apache.avro.Schema;
import org.apache.avro.generic.GenericDatumReader;
import org.apache.avro.generic.GenericRecord;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import org.apache.avro.io.BinaryDecoder;
import org.apache.avro.io.Decoder;
import org.apache.avro.io.DecoderFactory;
import org.apache.kafka.common.config.SaslConfigs;
import org.apache.kafka.common.config.SslConfigs;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArrayDeserializer;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArraySerializer;
public class KafkaAvroConsumer {
public static final void main(String args[]) {
// MagicByte wire format configuration
// Schema Id length is 4
private static final int SCHEMA_ID_BYTES_LEN = Integer.BYTES;
/** Index into the message bytes for the location of the magic byte. */
private static final int BYTES_IDX_MAGICBYTE = 0;
/** Index into the message bytes for the start of the schema id. */
private static final int BYTES_IDX_SCHEMAID = BYTES_IDX_MAGICBYTE + 1;
/** Index into the message bytes for the start of the serialized mesage contents. */
private static final int BYTES_IDX_MSGDATA = BYTES_IDX_SCHEMAID + SCHEMA_ID_BYTES_LEN;
Schema.Parser schemaDefinitionParser = new Schema.Parser();
Schema schema = null;
try {
// read the schema file from the local file system (it is possible to get it directly from the registry as well)
schema = schemaDefinitionParser.parse(new File("<Avro_Schema_file.avsc>"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
// Use a bynary deserialiser
props.put("value.deserializer", ByteArrayDeserializer.class.getName());
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "<kafka-broker-host>:<port>");
props.put("client.id", "<counsumer-client-id>");
props.put(CommonClientConfigs.SECURITY_PROTOCOL_CONFIG, "SASL_SSL");
props.put(SaslConfigs.SASL_MECHANISM, "SCRAM-SHA-512");
props.put(SaslConfigs.SASL_JAAS_CONFIG, "org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username=\"<kafka-user>\" password=\"<kafka-password>\";");
// provides the truststore in order to provide the Kafka broker certificate when the SSL connection is setup
// I am using here a JKS (PKSC12 is also possible)
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_TYPE_CONFIG, "JKS");
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG, "myTrustStore.jks");
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG, "TrustStorePwd");
KafkaConsumer consumer = new KafkaConsumer<String, byte[]>(props);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singletonList("<Kafka-Topic-Name>"));
try {
GenericDatumReader<GenericRecord> reader = new GenericDatumReader<GenericRecord>(schema);
while(true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, byte[]> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, byte[]> record : records) {
byte[] value = record.value();
byte[] messagebytes = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, BYTES_IDX_MSGDATA, value.length);
// The payload is located after the MagicBytes.
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(messagebytes);
// The payload is serialized using a binary encoded format
Decoder decoder = DecoderFactory.get().binaryDecoder(bais, null);
GenericRecord genericRecord = reader.read(null, decoder);
// Do something with your record
System.out.println("print a field of your payload: " + genericRecord.get("<field-from-your-schema>"));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
consumer.close();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
Resources
Some additional resources.
Example of java code used for AppConnect Enterprise Java compute node written by Dale Lane. The Blog.
Information on Avro SerDes

Leave a comment